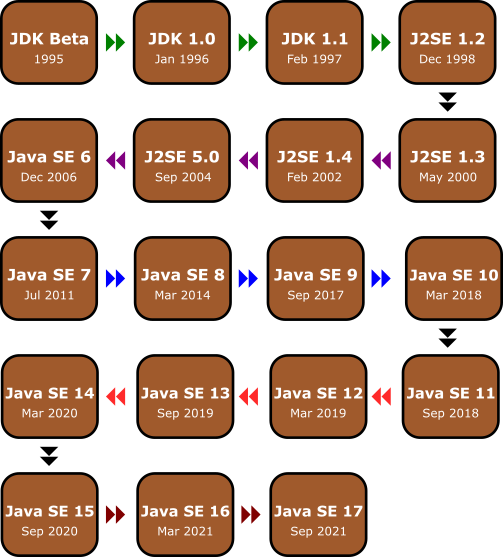
Java version history
Hello Readers, in this chapter we will see the various Java versions (+OpenJDK). For more information check on Wikipedia
Below is the chart showing the various version and release dates.
Below is brief description of these releases:
JDK 1.0
The first version was released on January 23, 1996. The first stable version, JDK 1.0.2, is called Java 1.
JDK 1.1
Major additions in the release on February 19, 1997 included:
- An extensive retooling of the AWT event model
- Inner classes added to the language
- JavaBeans
- JDBC
- RMI
- Reflection which supported Introspection only, no modification at runtime was possible.
- JIT (Just In Time) compiler.
- Internationalization and Unicode support.
J2SE 1.2 (Codename: Playground)
J2SE 1.2 released on December 8, 1998 . This was a very significant release of Java as it tripled the size of the Java platform to 1520 classes in 59 packages. Major additions included:
- strictfp keyword
- The Swing graphical API was integrated into the core classes
- Sun’s JVM was equipped with a JIT compiler for the first time
- Java plug-in
- Java IDL, an IDL implementation for CORBA interoperability
- Collections framework
J2SE 1.3 (Codename: Kestrel)
The most notable changes in the May 8, 2000 release were:
- HotSpot JVM included (the HotSpot JVM was first released in April 1999 for the J2SE 1.2 JVM)
- RMI was modified to support optional compatibility with CORBA
- Java Naming and Directory Interface (JNDI) included in core libraries (previously available as an extension)
- Java Platform Debugger Architecture (JPDA)
- JavaSound
- Synthetic proxy classes
J2SE 1.4 (Codename: Merlin)
The February 6, 2002 release was the first release of the Java platform developed under the Java Community Process as JSR 59.
Major changes included:
- assert keyword
- Regular expressions modeled after Perl regular expressions
- Exception chaining allows an exception to encapsulate original lower-level exception
- Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) support
- Non-blocking I/O (Java) (named NIO) (specified in JSR 51)
- Logging API (specified in JSR 47)
- Image I/O API for reading and writing images in formats like JPEG and PNG
- Integrated XML parser and XSLT processor (JAXP) (specified in JSR 5 and JSR 63)
- Integrated security and cryptography extensions (JCE, JSSE, JAAS)
- Java Web Start included (Java Web Start was first released in March 2001 for J2SE 1.3) (specified in JSR 56)
- Preferences API (java.util.prefs)
J2SE 5.0 (Codename: Tiger)
Tiger added a number of significant new language features:
- Generics: provides compile-time (static) type safety for collections and eliminates the need for most typecasts (type conversion) (specified by JSR 14)
- Metadata: also called annotations; allows language constructs such as classes and methods to be tagged with additional data, which can then be processed by metadata-aware utilities (specified by JSR 175)
- Autoboxing/unboxing: automatic conversions between primitive types (such as int) and primitive wrapper classes (such as Integer) (specified by JSR 201)
- Enumerations: the enum keyword creates a typesafe, ordered list of values (such as Day.MONDAY, Day.TUESDAY, etc.); previously this could only be achieved by non-typesafe constant integers or manually constructed classes (typesafe enum pattern) (specified by JSR 201)
- Varargs: the last parameter of a method can now be declared using a type name followed by three dots (e.g. void drawtext(String… lines)); in the calling code any number of parameters of that type can be used and they are then placed in an array to be passed to the method, or alternatively the calling code can pass an array of that type
- Enhanced for each loop: the for loop syntax is extended with special syntax for iterating over each member of either an array or any Iterable, such as the standard Collection classes (specified by JSR 201)
- Improved semantics of execution for multi-threaded Java programs; the new Java memory model addresses issues of complexity, effectiveness, and performance of previous specifications
- Static imports
- Automatic stub generation for RMI objects
- Swing: New skinnable look and feel, called synth
- The concurrency utilities in package java.util.concurrent
- Scanner class for parsing data from various input streams and buffers
Java SE 6 (Codename: Mustang)
Major changes included in this version:
- Scripting Language Support (JSR 223): Generic API for tight integration with scripting languages, and built-in Mozilla JavaScript Rhino integration.
- Dramatic performance improvements for the core platform, and Swing.
- Improved Web Service support through JAX-WS (JSR 224).
- JDBC 4.0 support (JSR 221).
- Java Compiler API (JSR 199): an API allowing a Java program to select and invoke a Java Compiler programmatically.
- Upgrade of JAXB to version 2.0: Including integration of a StAX parser.
- Support for pluggable annotations (JSR 269).
- Many GUI improvements, such as integration of SwingWorker in the API, table sorting and filtering, and true Swing double-buffering (eliminating the gray-area effect).
- JVM improvements include: synchronization and compiler performance optimizations, new algorithms and upgrades to existing garbage collection algorithms, and application start-up performance.
Java SE 7 (Codename: Dolphin)
Additions in Java 7 include:
- JVM support for dynamic languages, with the new invokedynamic bytecode under JSR-292, following the prototyping work currently done on the Multi Language Virtual Machine
- Compressed 64-bit pointers (available in Java 6 with -XX:+UseCompressedOops)
- Concurrency utilities
- New file I/O library (defined by JSR 203) adding support for multiple file systems, file metadata and symbolic links. The new packages are java.nio.file, java.nio.file.attribute and java.nio.file.spi
- Timsort is used to sort collections and arrays of objects instead of merge sort
- Library-level support for elliptic curve cryptography algorithms
- An XRender pipeline for Java 2D, which improves handling of features specific to modern GPUs
- New platform APIs for the graphics features originally implemented in version 6u10 as unsupported APIs
- Enhanced library-level support for new network protocols, including SCTP and Sockets Direct Protocol
- Upstream updates to XML and Unicode
- Java deployment rule sets
Java SE 8
Work on features was organized in terms of JDK Enhancement Proposals (JEPs).
- JSR 335, JEP 126: Language-level support for lambda expressions (officially, lambda expressions; unofficially, closures) under Project Lambda and default methods (virtual extension methods) which allow the addition of methods to interfaces without breaking existing implementations. There was an ongoing debate in the Java community on whether to add support for lambda expressions. Sun later declared that lambda expressions would be included in Java and asked for community input to refine the feature. Supporting lambda expressions also enables functional-style operations on streams of elements, such as MapReduce-inspired transformations on collections. Default methods allow an author of an API to add new methods to an interface without breaking the old code using it. Although it was not their primary intent, default methods also allow multiple inheritance of behavior (but not state).
- JSR 223, JEP 174: Project Nashorn, a JavaScript runtime which allows developers to embed JavaScript code within applications
- JSR 308, JEP 104: Annotation on Java types
- Unsigned integer arithmetic
- JSR 337, JEP 120: Repeating annotations
- JSR 310, JEP 150: Date and time API
- JEP 178: Statically-linked JNI libraries
- JEP 153: Launch JavaFX applications (direct launching of JavaFX application JARs)
- JEP 122: Remove the permanent generation
Java SE 9
- JSR 376: Modularization of the JDK under Project Jigsaw (Java Platform Module System)
- JavaDB was removed from JDK
- JEP 193: Variable handles : define a standard means to invoke the equivalents of various java.util.concurrent.atomic and sun.misc.Unsafe operations
- JEP 213: Milling Project Coin : Allow @SafeVarargs on private instance methods; Allow effectively-final variables to be used as resources in the try-with-resources statement; Allow diamond with anonymous classes if the argument type of the inferred type is denotable; Complete the removal, begun in Java SE 8, of underscore from the set of legal identifier names; Support for private methods in interfaces
- JEP 222: jshell: The Java Shell (Read-Eval-Print Loop) : JShell is a REPL command-line interface for the Java language.
- JEP 254: Compact Strings
- JEP 263: HiDPI graphics: automatic scaling and sizing
- JEP 266: More concurrency updates : It includes a Java implementation of Reactive Streams,[307] including a new Flow class that included the interfaces previously provided by Reactive Streams
- JEP 268: XML catalogs
- JEP 282: jlink: The Java Linker : create a tool that can assemble and optimize a set of modules and their dependencies into a custom run-time image. It effectively allows to produce a fully usable executable including the JVM to run it
- JEP 295: Ahead-of-Time Compilation : Ahead-of-time compilation provided by GraalVM.
Java SE 10
- JEP 286: Local-Variable Type Inference
- JEP 296: Consolidate the JDK Forest into a Single Repository
- JEP 304: Garbage-Collector Interface
- JEP 307: Parallel Full GC for G1
- JEP 310: Application Class-Data Sharing
- JEP 312: Thread-Local Handshakes
- JEP 313: Remove the Native-Header Generation Tool (javah)
- JEP 314: Additional Unicode Language-Tag Extensions
- JEP 316: Heap Allocation on Alternative Memory Devices
- JEP 317: Experimental Java-Based JIT Compiler
- JEP 319: Root Certificates
Java SE 11
- JEP 181: Nest-Based Access Control
- JEP 309: Dynamic Class-File Constants
- JEP 315: Improve Aarch64 Intrinsics
- JEP 318: Epsilon: A No-Op Garbage Collector
- JEP 320: Remove the Java EE and CORBA Modules
- JEP 321: HTTP Client (Standard)
- JEP 323: Local-Variable Syntax for Lambda Parameters
- JEP 324: Key Agreement with Curve25519 and Curve448
- JEP 327: Unicode 10
- JEP 328: Flight Recorder
- JEP 329: ChaCha20 and Poly1305 Cryptographic Algorithms
- JEP 330: Launch Single-File Source-Code Programs
- JEP 331: Low-Overhead Heap Profiling
- JEP 332: Transport Layer Security (TLS) 1.3
- JEP 333: ZGC: A Scalable Low-Latency Garbage Collector (Experimental)
- JEP 335: Deprecate the Nashorn JavaScript Engine
- JEP 336: Deprecate the Pack200 Tools and API
Java SE 12
- JEP 189: Shenandoah: A Low-Pause-Time Garbage Collector (Experimental)
- JEP 230: Microbenchmark Suite
- JEP 325: Switch Expressions (Preview)
- JEP 334: JVM Constants API
- JEP 340: One AArch64 Port, Not Two
- JEP 341: Default CDS Archives
- JEP 344: Abortable Mixed Collections for G1
- JEP 346: Promptly Return Unused Committed Memory from G1
Java SE 13
- JEP 350: Dynamic CDS Archives
- JEP 351: ZGC: Uncommit Unused Memory
- JEP 353: Reimplement the Legacy Socket API
- JEP 354: Switch Expressions (Preview)
- JEP 355: Text Blocks (Preview)
Java SE 14
- JEP 305: Pattern Matching for instanceof (Preview)
- JEP 343: Packaging Tool (Incubator)
- JEP 345: NUMA-Aware Memory Allocation for G1
- JEP 349: JFR Event Streaming
- JEP 352: Non-Volatile Mapped Byte Buffers
- JEP 358: Helpful NullPointerExceptions
- JEP 359: Records (Preview)
- JEP 361: Switch Expressions (Standard)
- JEP 362: Deprecate the Solaris and SPARC Ports
- JEP 363: Remove the Concurrent Mark Sweep (CMS) Garbage Collector
- JEP 364: ZGC on macOS
- JEP 365: ZGC on Windows
- JEP 366: Deprecate the ParallelScavenge + SerialOld GC Combination
- JEP 367: Remove the Pack200 Tools and API
- JEP 368: Text Blocks (Second Preview)
- JEP 370: Foreign-Memory Access API (Incubator)
Java SE 15
- JEP 339: Edwards-Curve Digital Signature Algorithm (EdDSA)
- JEP 360: Sealed Classes (Preview)
- JEP 371: Hidden Classes
- JEP 372: Remove the Nashorn JavaScript Engine
- JEP 373: Reimplement the Legacy DatagramSocket API
- JEP 374: Disable and Deprecate Biased Locking
- JEP 375: Pattern Matching for instanceof (Second Preview)
- JEP 377: ZGC: A Scalable Low-Latency Garbage Collector
- JEP 378: Text Blocks
- JEP 379: Shenandoah: A Low-Pause-Time Garbage Collector
- JEP 381: Remove the Solaris and SPARC Ports
- JEP 383: Foreign-Memory Access API (Second Incubator)
- JEP 384: Records (Second Preview)
- JEP 385: Deprecate RMI Activation for Removal
Java SE 16
- JEP 338: Vector API (Incubator)
- JEP 347: Enable C++14 Language Features
- JEP 357: Migrate from Mercurial to Git
- JEP 369: Migrate to GitHub
- JEP 376: ZGC: Concurrent Thread-Stack Processing
- JEP 380: Unix-Domain Socket Channels
- JEP 386: Alpine Linux Port – not yet stable
- JEP 387: Elastic Metaspace
- JEP 388: Windows/AArch64 Port
- JEP 389: Foreign Linker API (Incubator)
- JEP 390: Warnings for Value-Based Classes
- JEP 392: Packaging Tool
- JEP 393: Foreign-Memory Access API (Third Incubator)
- JEP 394: Pattern Matching for instanceof
- JEP 395: Records
- JEP 396: Strongly Encapsulate JDK Internals by Default
- JEP 397: Sealed Classes (Second Preview)
Java SE 17
- JEP 306: Restore Always-Strict Floating-Point Semantics
- JEP 356: Enhanced Pseudo-Random Number Generators
- JEP 382: New macOS Rendering Pipeline
- JEP 391: macOS/AArch64 Port
- JEP 398: Deprecate the Applet API for Removal
- JEP 403: Strongly Encapsulate JDK Internals
- JEP 406: Pattern Matching for switch (Preview)
- JEP 407: Remove RMI Activation
- JEP 409: Sealed Classes
- JEP 410: Remove the Experimental AOT and JIT Compiler
- JEP 411: Deprecate the Security Manager for Removal
- JEP 412: Foreign Function & Memory API (Incubator)
- JEP 414: Vector API (Second Incubator)
- JEP 415: Context-Specific Deserialization Filters
Latest Topics: